benedict's test positive color|5 minute timed writings : Bacolod Benedict’s solution is a deep-blue alkaline solution used to test for the presence of the aldehyde functional group, – CHO. One litre . Tingnan ang higit pa ENNS 2021 FF2023-50: Nutritional Status of Preschool Filipino Children One in every five (21.6%) infants and young children (0-23 months old) suffers from stunting, according to the 2021 Expanded National Nutrition Survey (ENNS) of the Food and Nutrition Research Institute (FNRI). Stunting is also common among preschoolers as the same survey .
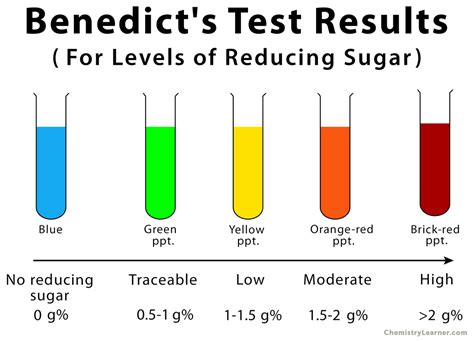
benedict's test positive color,If the color upon boiling is changed into green, then there would be 0.1 to 0.5 percent sugar in solution. If it changes color to yellow, then 0.5 to 1 percent sugar is present. If it changes to orange, then it means that 1 to 1.5 percent sugar is present. If color changes to red,then 1.5 to 2.0 percent sugar is . Tingnan ang higit paWhen Benedict’s solution and simple carbohydrates are heated, the solution changes to orange red/ brick red. This reaction is caused by the reducing property of . Tingnan ang higit paBenedict’s solution is a deep-blue alkaline solution used to test for the presence of the aldehyde functional group, – CHO. One litre . Tingnan ang higit pa Any change in color from blue to green or yellow or orange or red within 3 minutes indicates a positive Benedict test i.e. presence of reducing sugar in the .

When exposed to reducing sugars, the reactions undergone by Benedict’s reagent result in the formation of a brick-red precipitate, which indicates a positive Benedict’s test. An .
Benedict's reagent (often called Benedict's qualitative solution or Benedict's solution) is a chemical reagent and complex mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. It is often used in place of Fehling's solution to detect the presence of reducing sugars. The presence of other reducing substances also gives a positive result. Such tests that use this reag. Benedict’s test relies on the ability of reducing sugars to reduce cupric ions (Cu²⁺) present in Benedict’s solution, resulting in a color change from blue to green, yellow, orange, or even brick-red, . Observation and result interpretation: Positive Benedict’s test: color change from blue to brick red precipitate (glucose) Negative Benedict’s test: no change in color (sucrose) and water.5 minute timed writingsBenedict’s test is a simple chemistry test used to detect reducing sugars. Reducing sugars are carbohydrates having free aldehyde or ketone functional groups in their molecular structure. These include .Benedict's test positive on the left and negative on the right. Reference. Benedict's test is a simple chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars. .In this A-Level Biology Lesson "The Benedict's Test for Reducing and Non-Reducing sugars” you'll learn what makes a Reducing sugar a Reducing sugar. Next Non .
Benedict's solution is a blue colored liquid that contains copper sulfate. Copper binds to oxygen in the free aldehyde or ketone group forming a copper oxide. The copper oxide . Procedure. Add 1 ml of the sample to a test tube. Then add 2 ml of Benedict’s reagent. Mix the contents thoroughly. Heat the solution in a boiling water bath for 3 minutes. The formation of a red .benedict's test positive color 5 minute timed writings Pipette 5 ml of Benedict’s reagent in a test tube (20x150mm). Add 8 drops of urine to the Benedict’s reagent. Heat carefully on a flame of a gas burner or place in a boiling water for 5-10 minutes. Cool under tap water or by placing in a beaker containing tap water. Observe the color change and precipitate formation and analyse the test result. Procedure of Benedict’s Test. Take 1ml of sample in a dry test tube. Take 1ml of 5% glucose and 1ml distilled water in two separate dry test tubes. Add 2ml of benedict’s reagent to all the test tubes. .
Serial dilutions. Serial dilutions are created by taking a series of dilutions of a stock solution. The concentration decreases by the same quantity between each test tube. They can either be ‘doubling dilutions’ (where the concentration is halved between each test tube) or a desired range (e.g. 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 mmol dm-3); Serial dilutions are completed to create .
Positive Benedict’s test: color change from blue to brick red precipitate (glucose) Negative Benedict’s test: no change in color (sucrose) and water; Since the intensity of red color and the volume of precipitate change with the concentration of reducing sugar in the solution, the result can be further interpreted as:The Benedict’s Test is a method used to detect the presence of reducing sugars in a given sample. It involves the addition of Benedict’s reagent, which is a mixture of sodium citrate, sodium carbonate, and copper (II) sulfate, to a solution containing reducing sugars. The reducing sugars are capable of reducing copper (II) ions to copper (I .
Method. Add Benedict's reagent (which is blue as it contains copper (II) sulfate ions) to a sample solution in a test tube. It is important that an excess of Benedict’s solution is used so that there is more than enough copper (II) sulfate present to react with any sugar present. Heat the test tube in a water bath or beaker of water that has . The Benedict’s test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of reducing sugars, such as glucose, in a solution. The color change in the Benedict’s test indicates the presence and concentration of reducing sugars. Typically, a positive Benedict’s test results in a color change from blue to green, yellow, orange, or red, .Summary. Monosaccharides are crystalline solids at room temperature and quite soluble in water. Monosaccharides are reducing sugars; they reduce mild oxidizing agents, such as Tollens’ or Benedict’s reagents. 14.5: Properties of Monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are crystalline solids at room temperature and quite soluble in water. Benedict’s reagent is actually semi-qualitative as it has the ability to form different colors based on the concentration of reducing sugars. Green indicates about 0.5% reducing sugar concentration; .
Testing a urine sample with Benedict's reagent is a simple way of checking for the presence of glucose in people who are suspected of having this disease. It is, however, not a definitive test, . Procedure of Benedict’s Test. 1 mL of the sample solution should be added to a clean test tube (urine or carbohydrate solution). Pour two millilitres of Benedict’s reagents over the sample. Warm up the test tube either directly over a flame or over a pan of boiling water for three to five minutes. Watch for any changes in colour.
Put about 10 drops of Benedict’s reagent in the test tube. Bring the solution to heat in a boiling water bath for approximately five minutes. Observe for changes in color and watch out for precipitate formation. (4, 8, 9) Benedict’s test results. Image 4: The image shows the varying results of Benedict’s test. Picture Source . Figure 6.48: a) Heating the Benedict's solution in a boiling water bath, b) Benedict's test results: left tube is sucrose (negative), right tube is glucose (positive), c) Negative result, d) Positive result. Conjugated aldehydes are unreactive in the Benedict's test, and the author found many non-conjugated aldehydes to also be unreactive.The Benedict’s test for non-reducing sugars: -. Heat the test sample with dilute hydrochloric acid. Neutralise the test sample by adding sodium hydrocarbonate. Heat the test sample with Benedict’s Reagent. Observe the colour change. A brick red precipitate indicates the presence of a reducing sugar.benedict's test positive color Fill in Table 1 to specify which tube will receive which test substance. Add the appropriate test solution to the level of the 1 cm line. Add Benedict's reagent to the 2 cm line of each tube. Mix gently. Record initial color in Table 5.1. This is the color after Benedict’s reagent has been added but before heat.

A positive test with Benedict’s reagent is shown by a color change from clear blue to brick-red with a precipitate. Generally, Benedict’s test detects the presence of aldehydes, alpha-hydroxy-ketones, and hemiacetals, including those that occur in .
benedict's test positive color|5 minute timed writings
PH0 · primary colors personality tool pdf
PH1 · how does benedict's test work
PH2 · how benedict's solution works
PH3 · faint positive after 10 minutes
PH4 · benedict's test for glucose
PH5 · benedict's solution tests
PH6 · benedict reaction
PH7 · Iba pa
PH8 · 5 minute timed writings